In the ever-evolving landscape of investment options, Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) have emerged as one of the most popular and versatile choices for both novice and seasoned investors alike. With their simplicity, liquidity, and potential for diversification, ETFs have revolutionized the way people invest in financial markets. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into what ETFs are, how they work, their benefits and drawbacks, and explore why they have become such a prominent fixture in investment portfolios worldwide.
Table of Contents
Understanding ETFs
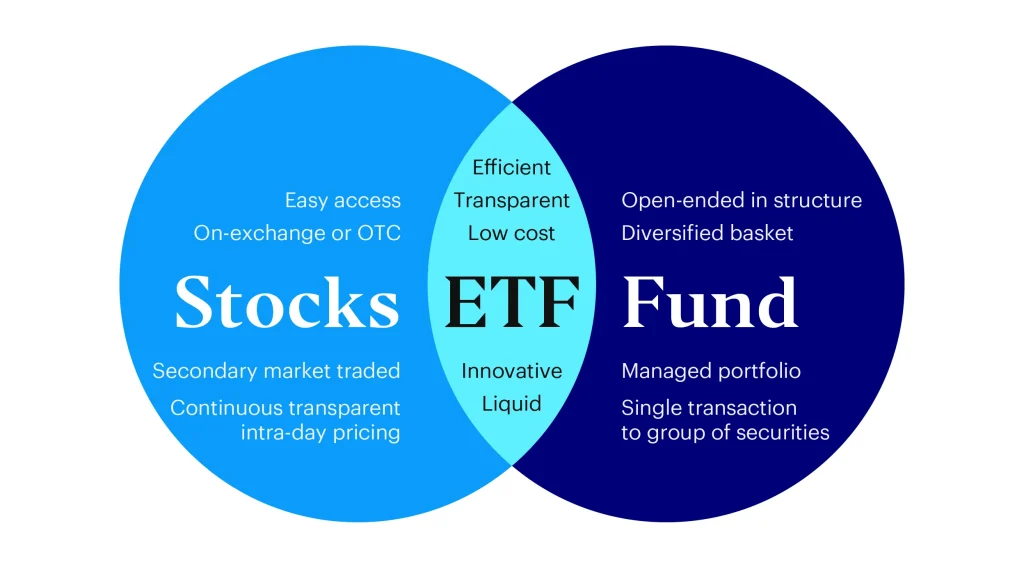
What is an ETF?
An Exchange Traded Fund (ETF) is a type of investment fund that holds assets such as stocks, commodities, or bonds and trades on stock exchanges much like individual stocks. Unlike traditional mutual funds, which are only priced at the end of each trading day, ETFs are traded throughout the day at market prices, providing investors with intraday liquidity.
How do ETFs work?
ETFs are designed to track the performance of a particular index, sector, commodity, or asset class. For example, a popular ETF like the SPDR S&P 500 ETF (SPY) aims to mirror the performance of the S&P 500 index. By investing in an ETF, investors gain exposure to a diversified portfolio of assets represented by the underlying index or assets held by the ETF.
Types of ETFs
ETFs come in various forms, catering to different investment objectives and strategies:
- Index ETFs: These ETFs aim to replicate the performance of a specific index, such as the S&P 500 or the Nasdaq-100.
- Sector ETFs: These focus on specific sectors of the economy, such as technology, healthcare, or energy.
- Bond ETFs: Bond ETFs invest in fixed-income securities like government bonds, corporate bonds, or municipal bonds.
- Commodity ETFs: These track the price movements of commodities like gold, silver, oil, or agricultural products.
- Inverse ETFs: These seek to profit from the decline in the value of an underlying index or asset.
- Leveraged ETFs: Leveraged ETFs use financial derivatives and debt to amplify the returns of an underlying index or asset.
Benefits of ETFs

Diversification
One of the primary advantages of investing in ETFs is diversification. Since ETFs typically hold a basket of securities, investors can spread their risk across multiple assets within a single investment, reducing the impact of volatility on their portfolio.
Liquidity
ETFs trade on major stock exchanges, providing investors with liquidity throughout the trading day. This means investors can buy or sell ETF shares at prevailing market prices, unlike traditional mutual funds, which are only priced once a day after the market closes.
Cost-Efficiency
ETFs often have lower expense ratios compared to mutual funds, making them a cost-effective investment option for investors. Additionally, since they are passively managed and aim to replicate the performance of an index, they tend to have lower management fees.
Transparency
ETFs disclose their holdings regularly, allowing investors to know exactly what assets they own within the fund. This transparency enables investors to make informed decisions about their investments and understand the underlying risks associated with the ETF.
Drawbacks of ETFs
While ETFs offer many benefits, they also come with certain drawbacks that investors should consider:
Tracking Error
Despite their objective to replicate the performance of an index, ETFs may not always perfectly track their underlying benchmark due to factors such as fees, trading costs, and market inefficiencies. This tracking error can result in deviations from the expected returns of the index.
Trading Costs
While ETFs provide intraday liquidity, investors may incur trading costs such as brokerage commissions and bid-ask spreads when buying or selling ETF shares. Frequent trading can erode returns, especially for smaller investors.
Complexity
Some ETFs, particularly leveraged and inverse ETFs, can be complex financial instruments that may not be suitable for all investors. These products require a deep understanding of their underlying strategies and risks, and novice investors may find them challenging to navigate.
Why ETFs are Popular
Flexibility
ETFs offer investors flexibility in terms of asset allocation, allowing them to easily adjust their exposure to various sectors, regions, or asset classes based on market conditions and investment objectives. This flexibility appeals to both individual investors and institutional investors managing large portfolios.
Accessibility
ETFs have democratized access to a wide range of investment opportunities that were previously inaccessible or costly for individual investors. With just a brokerage account, investors can gain exposure to global markets, commodities, and niche sectors with relative ease.
Tax Efficiency
ETFs are known for their tax efficiency compared to mutual funds, primarily due to their unique structure. Since ETFs typically have low turnover and can use in-kind creation and redemption processes to manage capital gains, they may generate fewer taxable distributions for investors.
Conclusion
Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) have revolutionized the way investors access financial markets, offering simplicity, liquidity, and diversification in a single investment vehicle. Whether you’re a novice investor looking to build a diversified portfolio or a seasoned investor seeking to fine-tune your asset allocation, ETFs provide a versatile and cost-effective solution. However, it’s essential to understand the risks and complexities associated with ETF investing and conduct thorough research before incorporating them into your investment strategy. With proper due diligence and a clear understanding of your investment goals, ETFs can be a valuable addition to your portfolio, helping you achieve your long-term financial objectives.
Do you want to know about mutual funds: https://paisainvests.com/mutual-funds/



